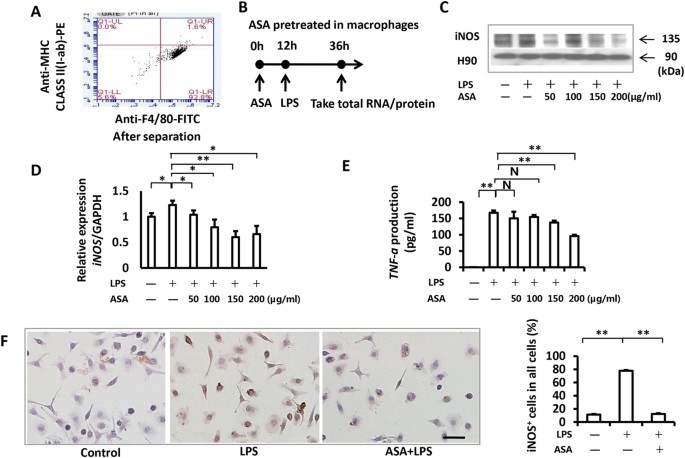
Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses by an Apolipoprotein AI Mimetic Peptide | Circulation Research
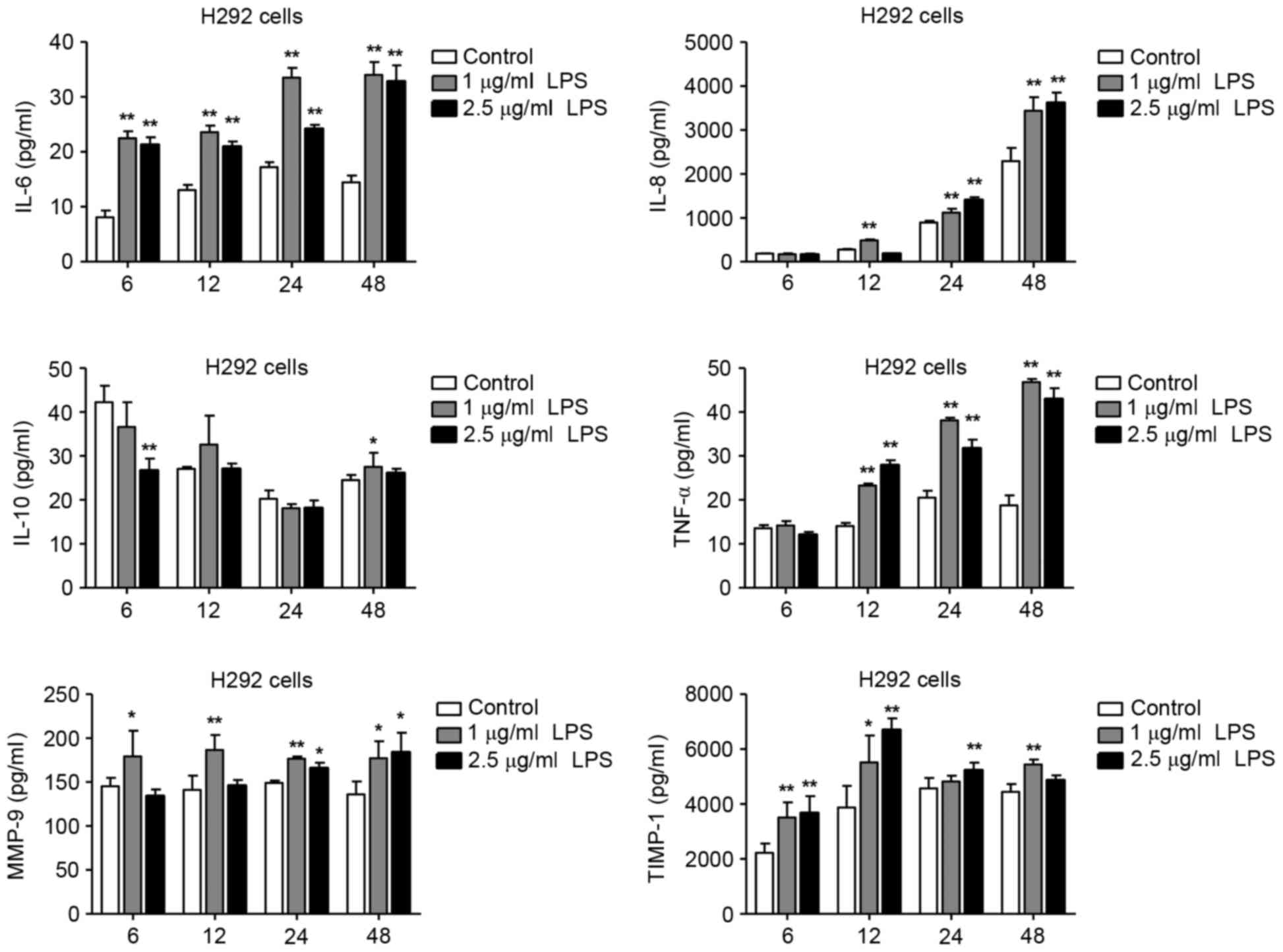
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation

Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Microglial Activation and Neuroprotection against Experimental Brain Injury Is Independent of Hematogenous TLR4 | Journal of Neuroscience
Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Expression of Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase-1 Mediates Late-Phase PGE2 Production in Bone Marrow Derived Macrophages | PLOS ONE

Lipopolysaccharide Administration Alters Extracellular Vesicles in Cell Lines and Mice | SpringerLink
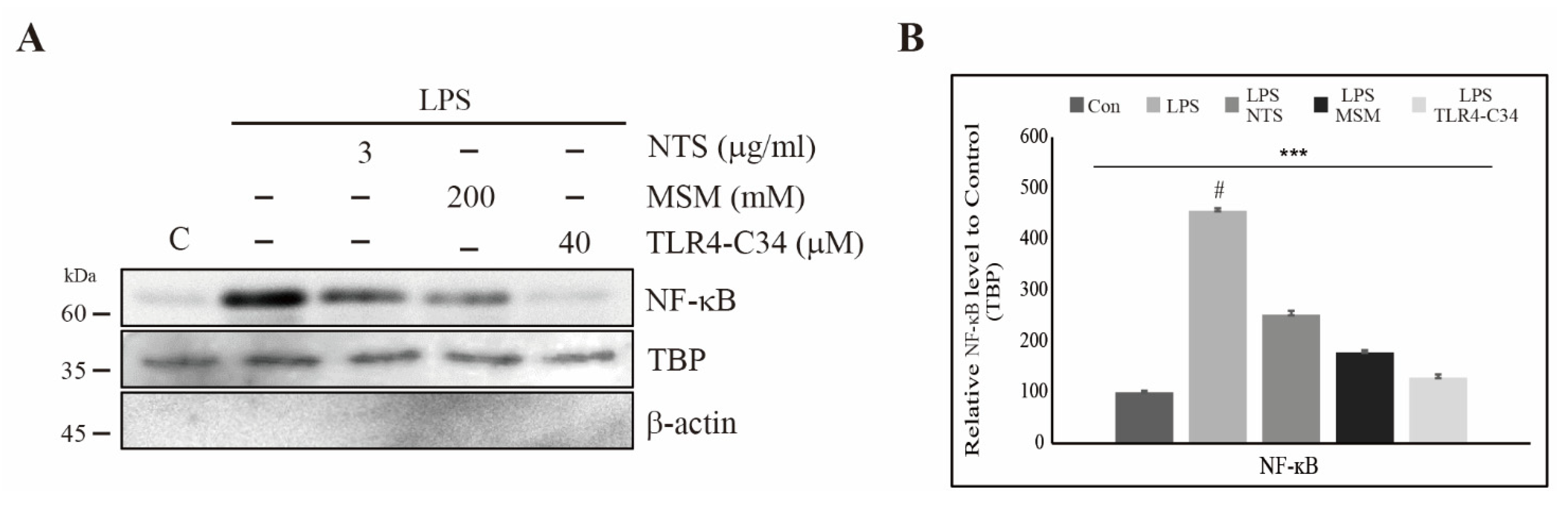
Life | Free Full-Text | Natural Sulfurs Inhibit LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through NF-κB Signaling in CCD-986Sk Skin Fibroblasts | HTML

Human monocytes respond to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation in a sex‐dependent manner - Campesi - 2022 - Journal of Cellular Physiology - Wiley Online Library
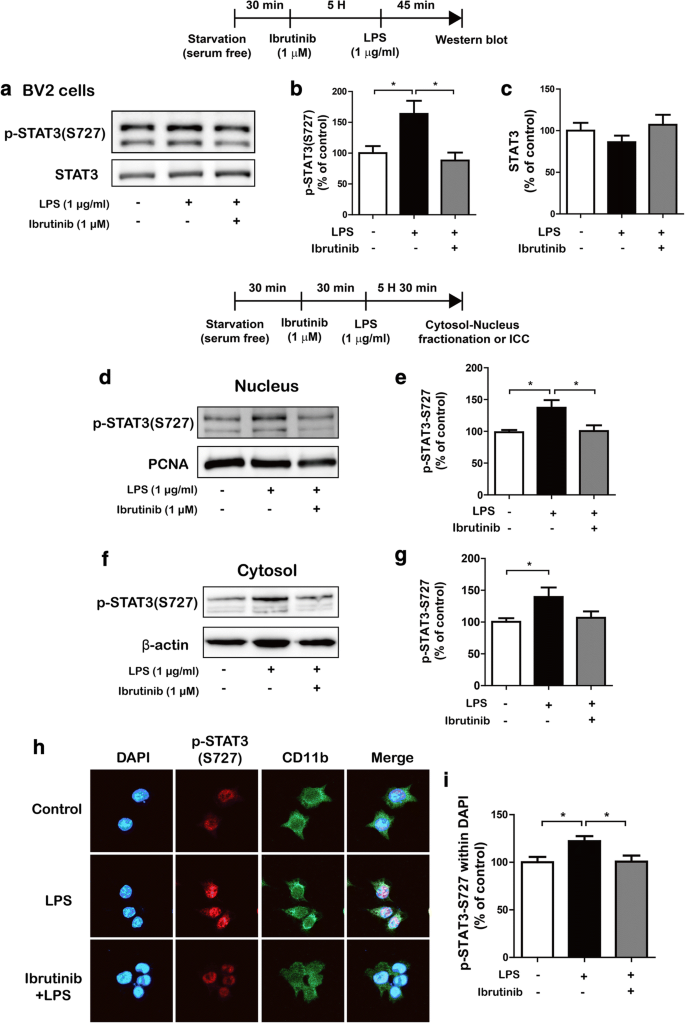
Ibrutinib suppresses LPS-induced neuroinflammatory responses in BV2 microglial cells and wild-type mice | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text

Induction of COX‐2 by LPS in macrophages is regulated by Tpl2‐dependent CREB activation signals | The EMBO Journal

Prostacyclin post-treatment improves LPS-induced acute lung injury and endothelial barrier recovery via Rap1 - ScienceDirect

Surfactant Protein A Enhances the Degradation of LPS-Induced TLR4 in Primary Alveolar Macrophages Involving Rab7, β-arrestin2, and mTORC1 | Infection and Immunity

Programming Effects of Pubertal Lipopolysaccharide Treatment in Male and Female CD-1 Mice | The Journal of Immunology

Lipopolysaccharide-induced Apoptosis of Macrophages Determines the Up-regulation of Concentrative Nucleoside Transporters Cnt1 and Cnt2 through Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-dependent and -independent Mechanisms* - Journal of Biological Chemistry
Effect of LPS-treatment on pro-inflammatory cytokine/chemokine levels.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Phosphorylated ERM Mediates Lipopolysaccharide Induced Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells Permeability Through Negatively Regulating Rac1 Activity | Archivos de Bronconeumología

LPS decreases fatty acid oxidation and nuclear hormone receptors in the kidney* - Journal of Lipid Research

Triptolide prevents LPS‐induced skeletal muscle atrophy via inhibiting NF‐κB/TNF‐α and regulating protein synthesis/degradation pathway - Fang - 2021 - British Journal of Pharmacology - Wiley Online Library
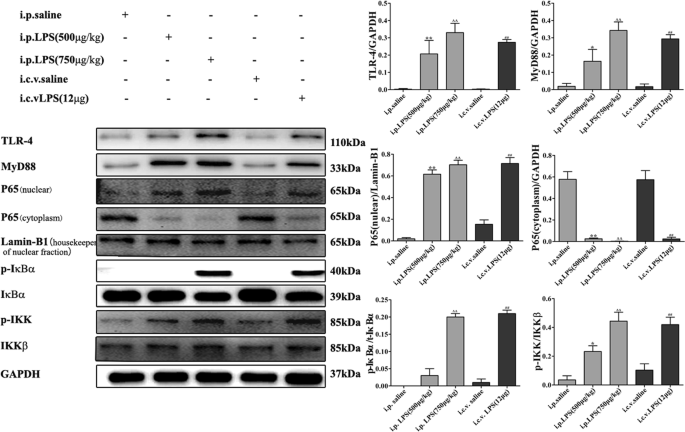
Neuroinflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment in mice | Scientific Reports

MAR1 suppresses inflammatory response in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages and human primary peripheral blood mononuclear cells via the SIRT1/PGC-1α/PPAR-γ pathway | Journal of Inflammation | Full Text

LPS-induced TNF-α factor (LITAF)-deficient mice express reduced LPS-induced cytokine: Evidence for LITAF-dependent LPS signaling pathways | PNAS
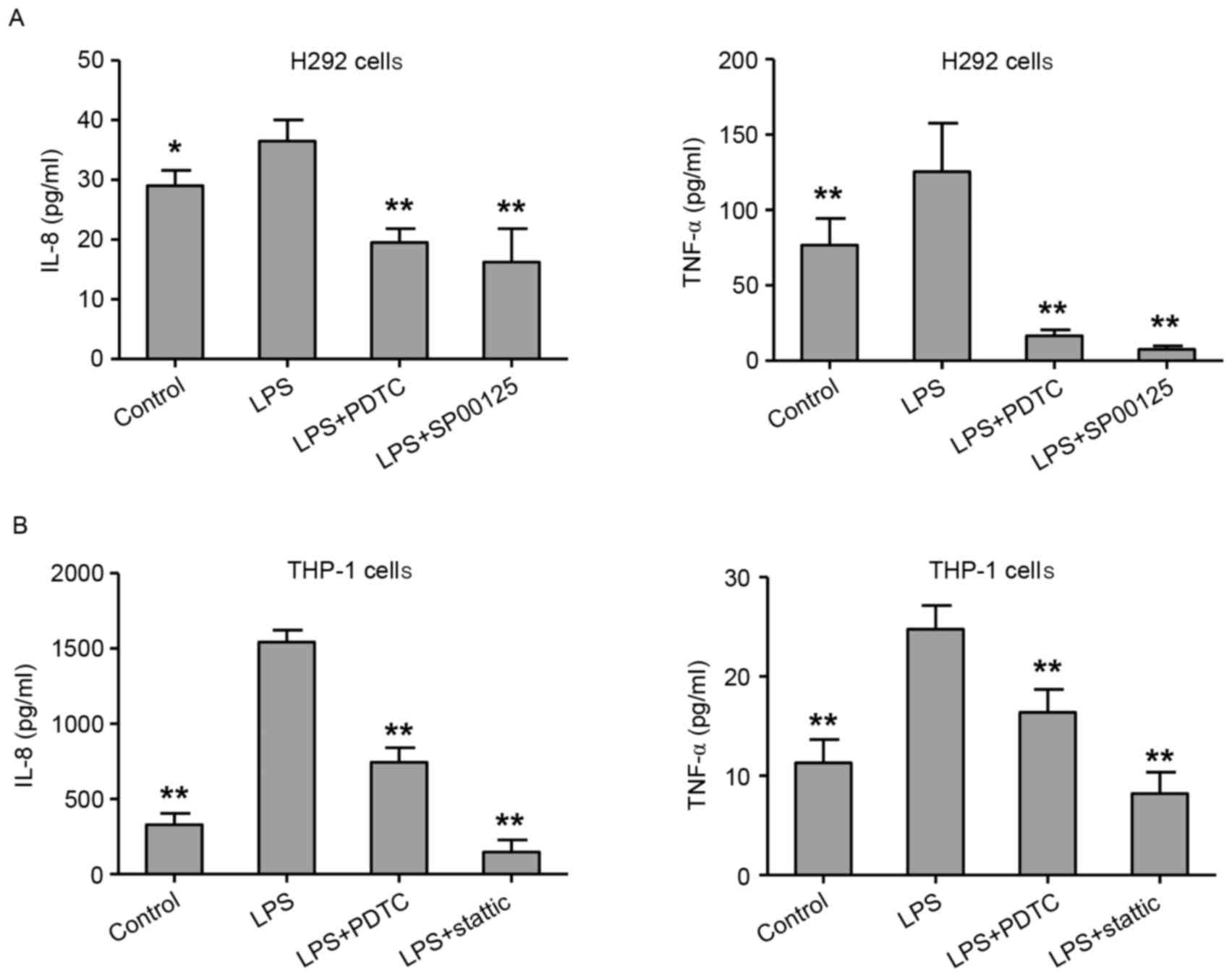
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Biliary Epithelial Cell NRas Activation Requires Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) | PLOS ONE
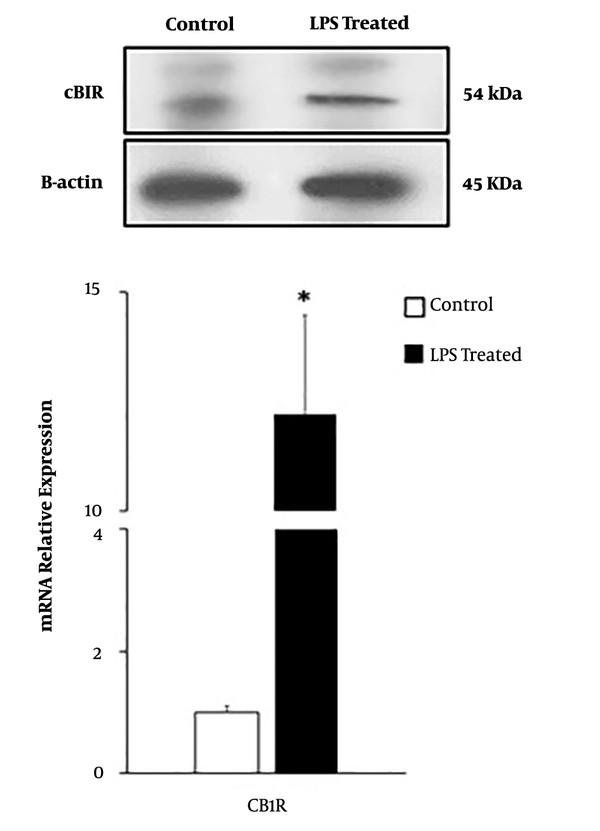
The LPS-Treated Human Gastric Cancer Cells (AGS) Show a Significant Higher Tendency to Proliferation, Inflammation and Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression | Jentashapir Journal of Cellular and Molecular Biology | Full Text
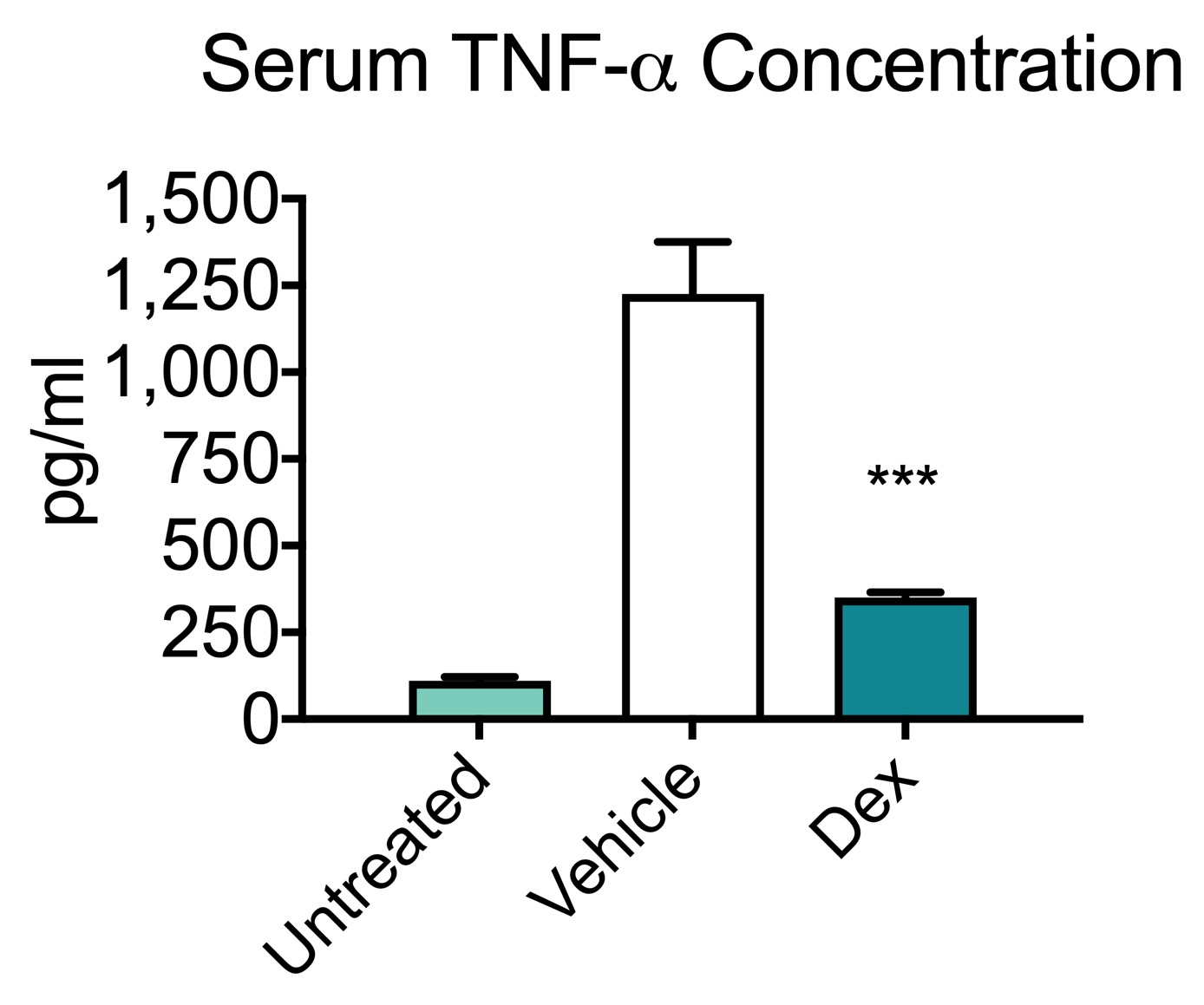
Dexmedetomidine inhibits LPS-induced proinflammatory responses via suppressing HIF1α-dependent glycolysis in macrophages | Aging